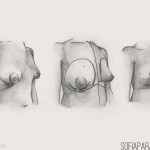
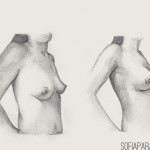
Implants have been used to enlarge the breast or reconstruct the breast for more than 40 years. Not only is size important but also shape. An appropriate sized breast for the size and type of body is very important for a good body image and confidence.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding can also alter the shape and size of the breast as well as normal ageing. Some patients may require a lift (see the section on mastopexy) in addition to more volume.
4a.Breast implants
A breast implant consists of an outer silicone elastomer shell, which can be filled with a variety of materials. The outer shell can be smooth walled or textured. Currently there are two fillers on the market – silicone or saline (salt water). Silicone is available as a gel or a cohesive gel. Implants can be round or shaped.
The surgeon prefers textured silicone implants. When an implant is inserted into the body a membrane forms around the implant in the same way as it forms around a knee prosthesis or any foreign body. The membrane or capsule normally stays soft and the patient is unaware of it. Sometimes, however, it may becomes thicker in some patients and cause asymmetry or pain. This may require further surgery. Textured implants are normally associated with a reduced risk of capsule formation.
The implant may be inserted through a little scar in the crease under the breast or through an incision around the areola. The implant may be inserted in a submuscular (under the chest muscle) or subglandular (under the breast tissue) position. The type of implant, the size of the implant as well as the position of placement and the type of incision will be discussed during the consultation. It varies greatly from patient to patient.
Mammography is possible after breast implants but with Magnetic resonance mammography. This imaging modality has the possibility to detect possible implant rupture and to clearly visualize dense breasts with silicone implants. The disadvantage is the cost of the examination, the use of contrast medium, the inability to detect calcifications <3mm and the duration of the examination.
Complications
The operation is usually free of complications but any of the following may occur:
• Capsular contracture
• Collection of blood around the implant (haematoma) from a blood vessel that has opened up which may require drainage
• Displacement of the implant
• Infection
• Changes in nipple sensation
• Wrinkling of the implant
The surgery
A general anaesthetic is normally required and can be performed as a day case. Pain is minimal to moderate and can be controlled by painkillers taken orally most of the time. The breasts are taped up during the surgery in a supportive bandage. The breasts will be swollen and tender and may feel very tight.
Complications
Capsular contracture (in some studies the rate is up to 20%)
Hematoma (blood collection under the implant) that needs to be drained
Implant migration
Infection
Altered nipple sensitivity (15%)
Implant rippling
24-33% of patients undergoing breast augmentation with silicone implants developed one of the above mentioned complications and need to be re-operated early or much later in their lives.
After the surgery
You can normally sit in a shallow bath but should not get the breasts, dressings or incision lines wet. The sutures will be removed after 10-12 days. You should refrain from doing heavy lifting or exercise for 4 weeks after the surgery. Massaging of the scars four weeks after the surgery will help the scar to fade quickly.
4b. Breast augmentation with lipotransfer
The surgery
It’s done under general anaesthesia and the patient spends one night in the hospital. Postoperative pain is moderate and can be controlled by tablets. The breasts are swollen and tender.
The fat is suctioned from pre-agreed areas of the abdomen and thighs through small 4-5mm incisions. After centrifugation fat is injected in different levels under the breast gland through small incisions.
During the operation an overcorrection is done since about 70% of the transferred fat cells will survive. The incisions are covered with small stere-strips and the breasts wrapped in a soft athletic type top.
The best candidates are patients from whom one can remove fat and are interested in a small augmentation (up to one cup)
Complications
According to the % of fat survival, a second session might be required. The small incision scars usually fade with time to normal skin color. Because of many levels of fat injection, though rare, the formation of lumps can occur. This usually resolves with massaging of the area. Swelling and bruises, subside within 10 days. You will receive prophylactic antibiotic treatment.
After the surgery
The fat remaining 3 months postoperatively is considered permanent. Sutures are removed after a week and you’ll be ready to return to your everyday schedule.