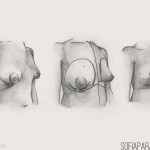
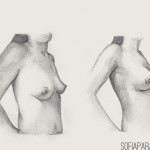
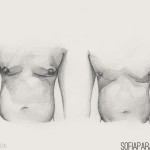
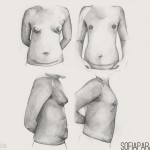
Breast reconstruction after cancer surgery should be offered to all suitable patients before surgery and adequately discussed. Therefore, a team approach involving breast surgeon, reconstructive plastic surgeon, oncologist, breast care nurse and various counsellors is of the utmost importance.
Since the early eighties it became clear that breast reconstruction performed at the time of mastectomy in cases of early breast cancer is indeed safe and not compromising the oncological treatment or outcome for the patient. Should immediate breast reconstruction be contra-indicated due to advanced disease or other problems then a delayed reconstruction is always an option once a disease free period has lapsed. Significant improvement in body image and quality of life scores have been shown in-patients after reconstruction especially the younger patient groups.
Several accepted surgical alternatives are available. Breast reconstruction after mastectomy neither prevents early detection of disease recurrence nor precludes the use of chemo or radiotherapy.
Once the necessity for surgery has been established a detailed discussion should follow regarding surgical options:
• lumpectomy with radiotherapy
• mastectomy
• mastectomy with breast reconstruction
Studies have shown this discussion is very important and only 40% of patients recalled mentioning breast reconstruction preoperatively and only 55% recall that lumpectomy had been discussed. This emphasizes the continuing inadequacy of patient information.
Whereas not all women may wish to assume an active role in treatment decision-making, it is important to be well informed about all options available.
Options available:
A. Implants
In small-breasted woman an implant only may be suitable which can be inserted through the incision that was used for the mastectomy. Silicone gel implants is currently available for use.
B. Tissue Expansion
A balloon type device is placed under the chest wall skin at the same operation that mastectomy is performed. It can be inflated after insertion to stretch the skin and produce more skin and improve symmetry with the other breast. Inflation or stretching is normally done over a period of time (with weekly visits at the office or out-patient department), until the right volume and amount of skin is reached, sometimes overcorrecting (to achieve a similar amount of droop to the healthy side). This option is not indicated if radiotherapy to the chest wall has been given or is to be done postoperatively.
C. Fat transfer
It’s indicated only in patients that have undergone skin sparring mastectomy so that their skin envelope is intact and have a small sized breast, up to cup B. It can be done at the same time with the mastectomy or later on but within time limits of 3-6 months in order to avoid skin and wound shrinkage. Liposuction is performed from the areas decided prior to surgery and the fat is injected in the skin pocket of the breast until the wanted size is reached. Fat is absorbed at some extent (up to 40%), therefore another session under sedation might be necessary.
D. Latissimus Dorsi Flap
The muscle from the back with an amount of back skin can be used to replace the skin taken during a mastectomy. An implant or fat from another site of the patient is normally used with it to provide the bulk for the newly created breast. This obviously leaves a linear scar on the back of the patient that is partly hidden by the bra.
E. TRAM Flap
Skin and fat from the lower abdomen can be used. The patient then has a “tummy tuck” type of scar on the lower abdomen. Enough tissue has to be available for transfer. No implant is used. There are 3 ways to transfer the flap:
1) It can be “pedicled”, that is stay attached to the donor area
2) Free flap, to totally separate it from the donor area, transfer it and re-attache it to the recipient area for it’s blood supply, under microscope
3) By the DIEP technique. By this method, no muscle is taken and the blood supply is re-attached under the microscope (DIEP).
The operation
The surgery can be performed at the time of the mastectomy or later during a second operation. Hospital stay varies with each technique and between patients and range from 3-7 days. Early postoperatively you will have surgical drains coming out of the wound to drain away excess fluid. These are normally removed on day 2 or 3 after the operation. Sutures are normally removed between 8-12 days post-surgery. A recovery period from between 6 weeks and 3 months should be expected.
Complications
Complications are increased in overweight patients, smokers and women who had undergone radiotherapy.
Conclusion
Breast reconstruction should be offered as an option to all patients undergoing mastectomy, partial mastectomy or lumpectomy. Recent studies have confirmed the belief that a woman undergoing breast reconstruction has significant psychological benefits. Patients undergoing immediate reconstruction did not show the same poorer preoperative body image compared to patients undergoing delayed reconstruction, however, both groups benefit significantly from reconstruction. The type of reconstruction does not appear to influence patient satisfaction.